Stream Configuration
Following sections describe how to configure Padas to run streaming tasks in order to transform events and/or apply a set of filtering rules to generate alerts. Please refer to Introduction before moving forward in order to understand engine processing concepts.
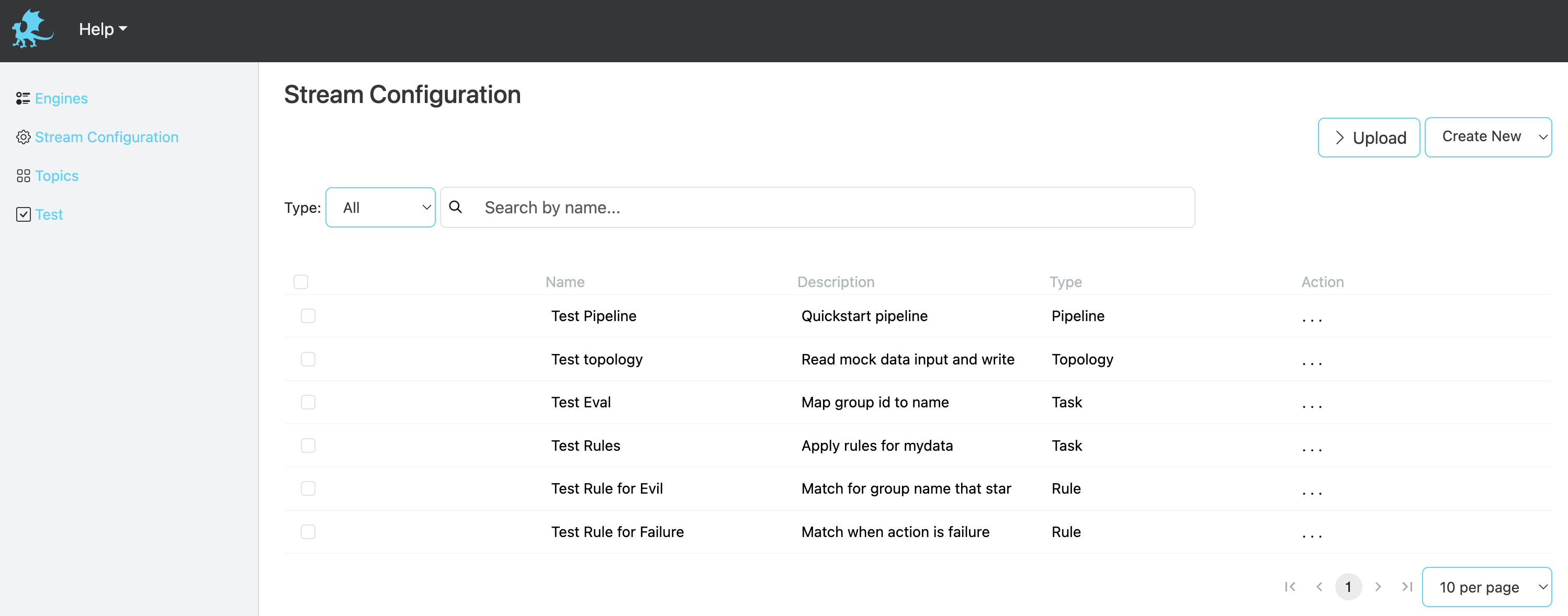
All of the configuration views (Topologies, Pipelines, Tasks, Rules) provide the ability to bulk upload or download configurations in JSON format. Note: Lookups are excluded from bulk upload/download functionality.
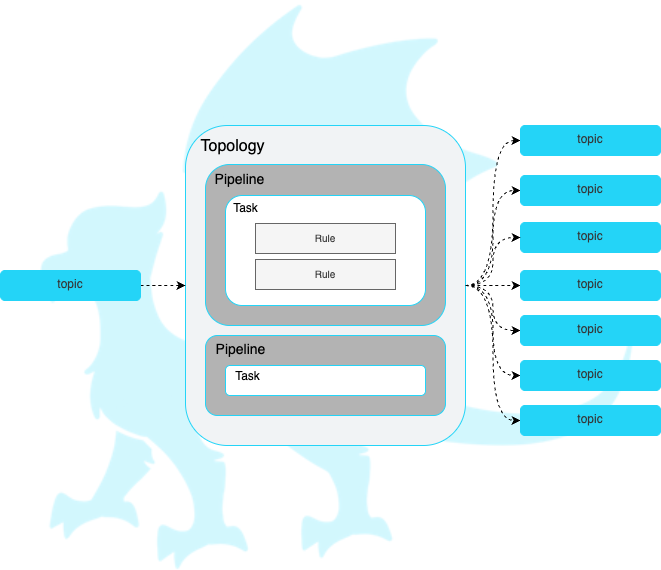
Topologies
A topology is simply a group of one or more ordered pipelines where it reads from a single input topic and writes to one or more output topic(s). Both input and output topic(s) are mandatory requirements for a topology that Padas engine runs. A topology consists of one or more ordered pipelines where an output from one pipeline becomes an input for the next pipeline definition.
It's possible to define any number of topologies per Padas Engine, where each topology starts a different processing task within one or more threads. For more detailed architectural description on Kafka streams processor topology please refer to Confluent Documentation.
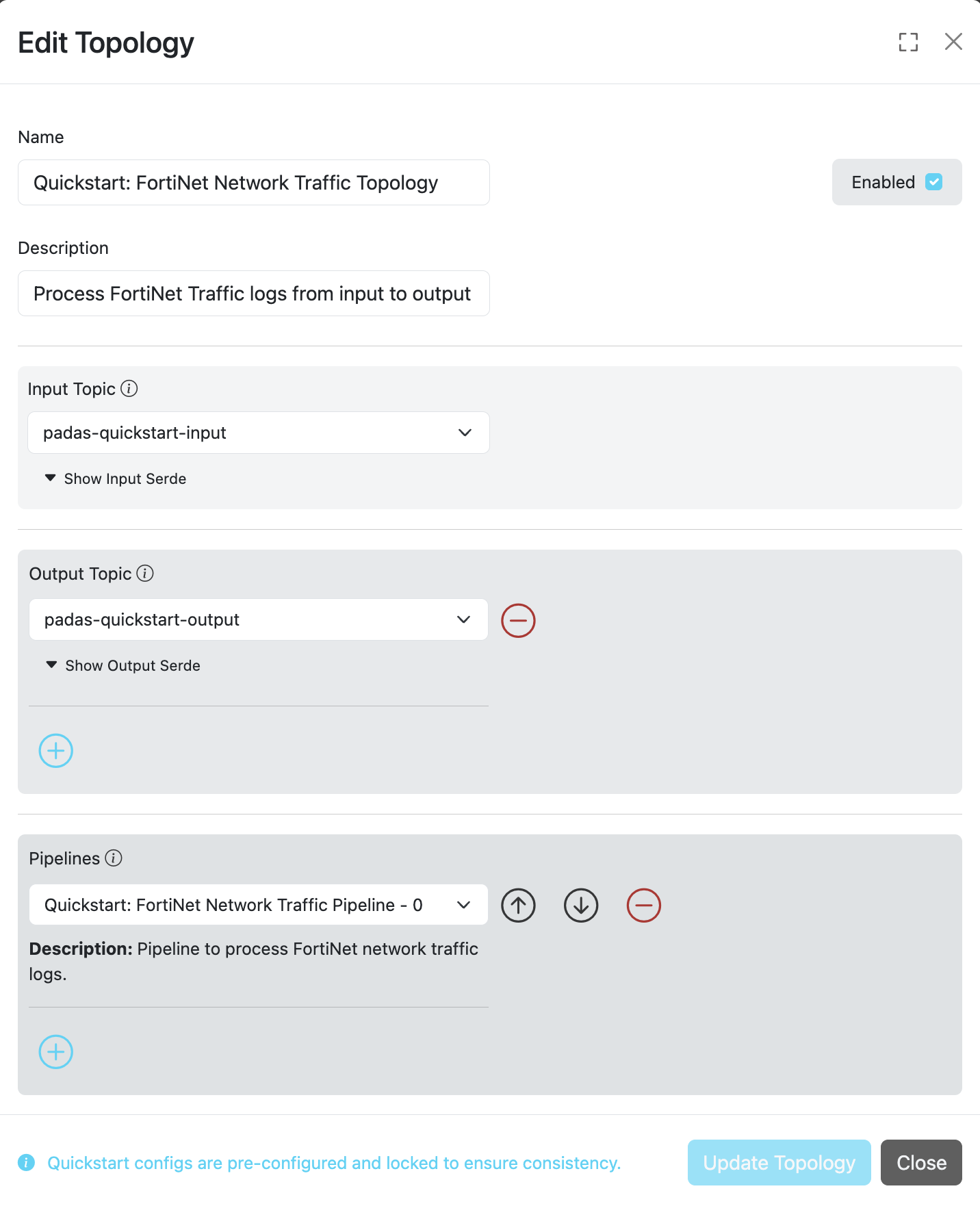
A comprehensive description of topology configuration fields is provided in the table below.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | String | ✓ | Unique identifier for the topology. This ID is also used as a key when updating or deleting the entry. |
| Name | String | ✓ | A descriptive name for the topology configuration. |
| Description | String | ✗ | Detailed description explaining the topology's functionality and purpose. |
| Group | String | ✓ | Consumer group associated with this topology for Kafka message consumption. |
| Input | String | ✓ | Input topic name from which data will be consumed and processed through the configured pipeline(s). |
| Output | String/Array | ✓ | One or more output topic names where transformed data will be sent after processing. |
| Enabled | Boolean | ✓ | Controls topology activation: true to enable, false to disable the topology. |
| Pipelines | Array | ✓ | An ordered list of pipeline IDs to execute when streaming data from the specified input topic. Processing Flow: When multiple pipelines are specified, the output from one pipeline becomes the input for the next pipeline in the sequence. |
Pipelines
A pipeline consists of one or more ordered tasks where an output from one task becomes an input for the next task definition. A pipeline is a logical grouping of tasks for specific goals. For example, in terms of processing tasks, a single pipeline with 12 different tasks is the same as having 3 consecutive pipelines with 4 different tasks each.
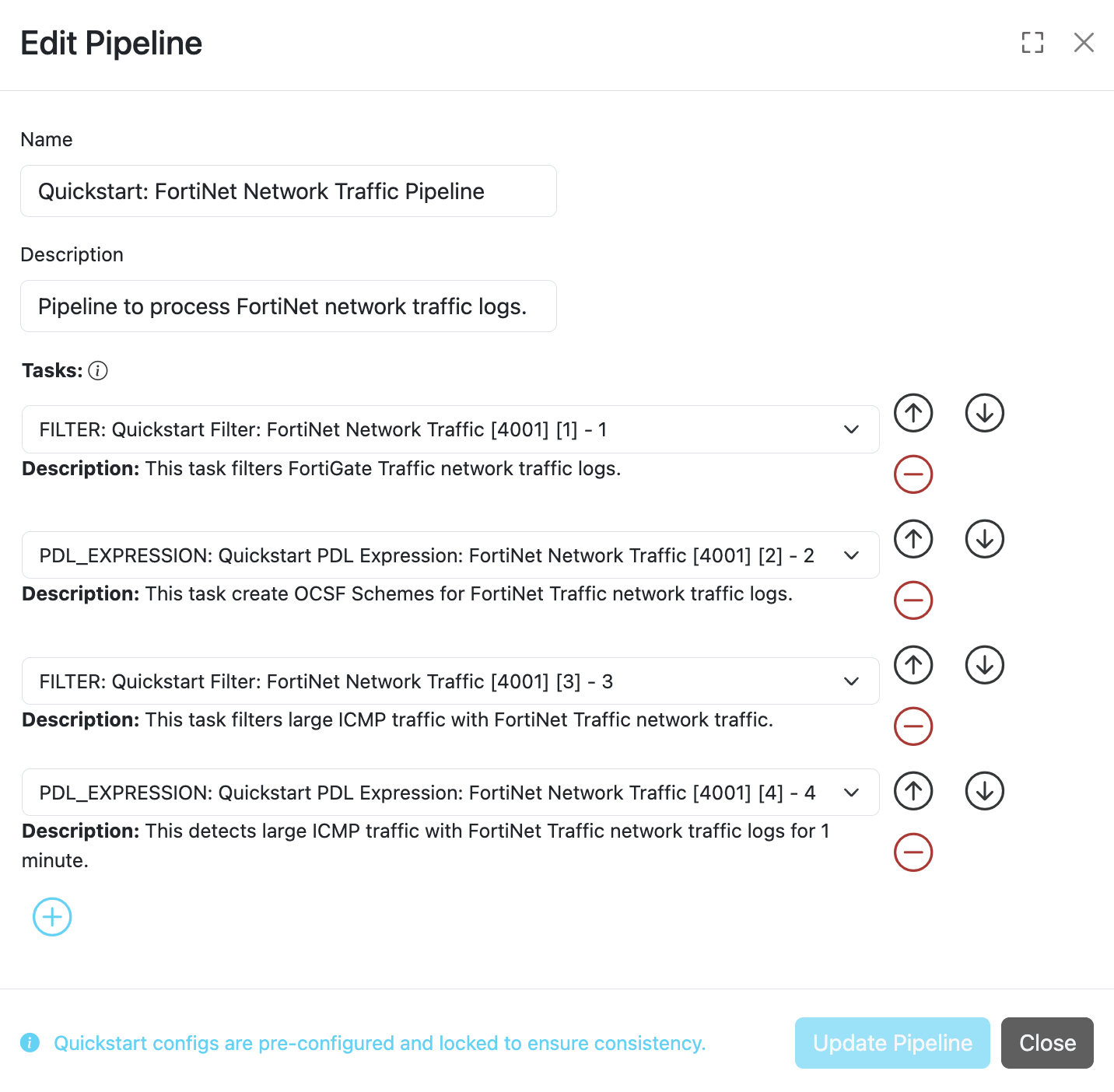
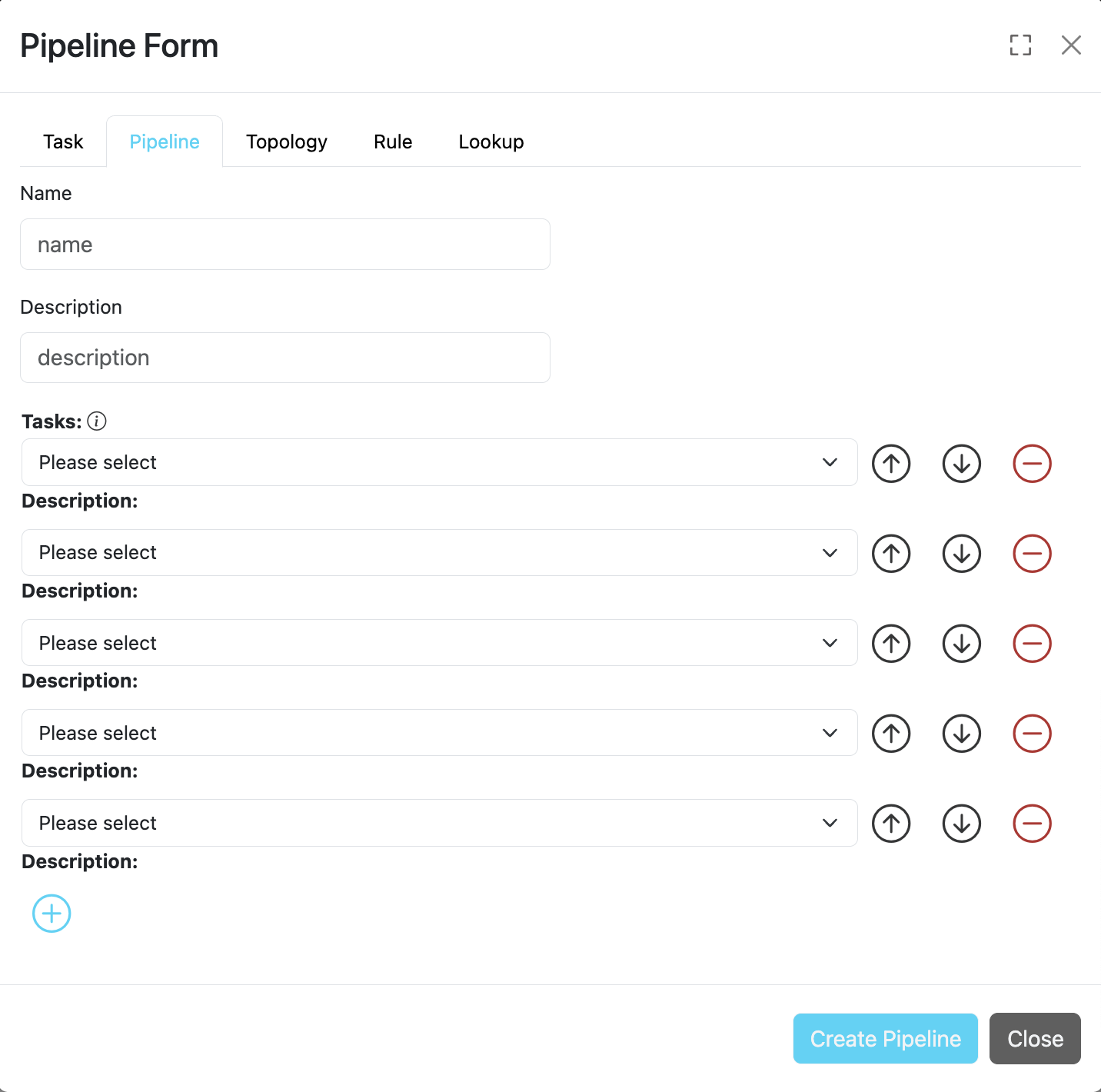
A comprehensive description of pipeline configuration fields is provided in the table below.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | String | ✓ | Unique identifier for the pipeline. This ID is also used as a key when updating or deleting the entry. |
| Name | String | ✓ | A descriptive name for the pipeline configuration. |
| Description | String | ✗ | Detailed description explaining the pipeline's functionality and purpose. |
| Tasks | Array | ✓ | An ordered list of task IDs to execute when processing data through this pipeline. Processing Flow: When multiple tasks are specified, the output from one task becomes the input for the next task in the sequence. |
Tasks
A task is the single unit of work performed on event data. Each task has the following built-in functions that can perform processing on an event:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | String | ✓ | Unique identifier for the task. This ID is also used as a key when updating or deleting the entry. |
| Name | String | ✓ | A descriptive name for the task configuration. |
| Description | String | ✗ | Detailed description explaining the task's functionality and purpose. |
| Function | String | ✓ | The task function to execute. Must be one of the following predefined functions: |
Available Task Functions
APPLY_RULES: Apply predefined rules (per event and/or correlated/aggregated) to streaming events. The input must beJSON.EXTRACT: Extract any event input with provided Regular Expression defition (named groups). The output isJSON.FILTER: Filter an event (keep or drop) based on PDL or regex definition. For PDL, the input must beJSON.OUTPUT_FIELD: Outputs the value of a given field. The input must beJSONand the output isStringrepresentation of the selected field value.PARSE_CEF: Parse input CEF (Common Event Format) event intoJSON.PARSE_CSV: Parse inputCSVevent intoJSON.PARSE_KV: Parse input key-value pairs event intoJSON.PDL_EXPRESSION: Allows event data transformation and enrichment via PDL expressions. The input must beJSON.TIMESTAMP: Define a field from within the event data (JSONformatted) to use as the timestamp.
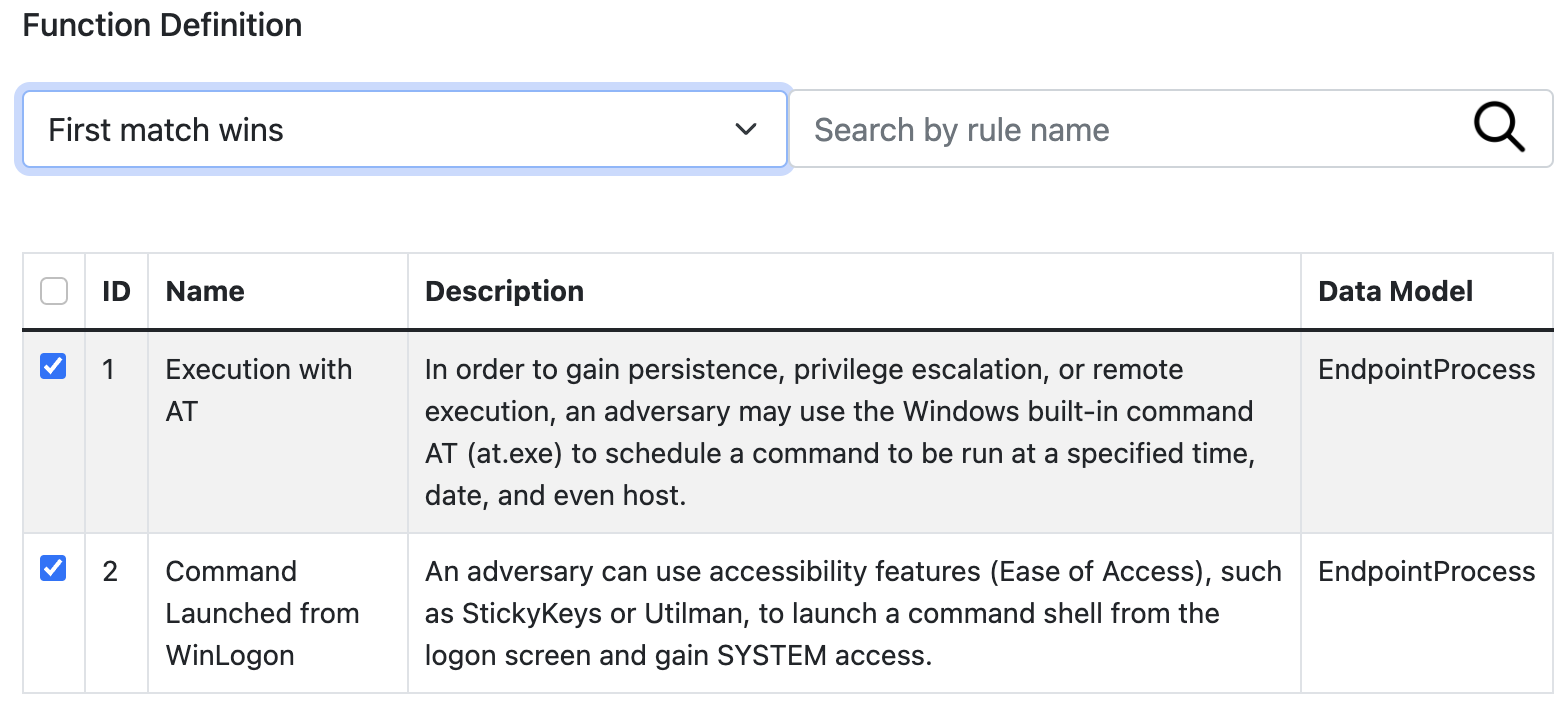
APPLY_RULES Definition
This function applies pre-defined rules (PDL queries) in order to generate event alerts that match them. The output is enriched with the padas_rules object array that contains matching rule information as well as the event data.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | String | ✓ | ID of the pre-defined rule. |
| Name | String | ✓ | Name of the pre-defined rule. |
| Description | String | ✗ | Description of the pre-defined rule. |
| Data Model | String | ✗ | Data model identifier for the rule processing context. |
| Rules | Array | ✓ | List of selected rules to process when this task is running. |
| Match All | String | ✓ | If set to Match all rules, all rules for this task are evaluated. If set to First match wins, evaluation stops. |
Example
EXTRACT Definition
This function allows usage of named capturing groups in regular expressions to extract fields from event data. The output is a JSON formatted event with named groups as fields.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regex | String | ✓ | Named group capturing Regular Expression to match the event. Captured named groups will be JSON field names. |
| Keep Raw | Boolean | ✓ | Boolean to keep raw data in a separate field. If set to true, a field name should be provided. |
| Raw Field Name | String | ✗ | If raw data is to be kept, this will be the field to store it in. _raw is the default. |
Example
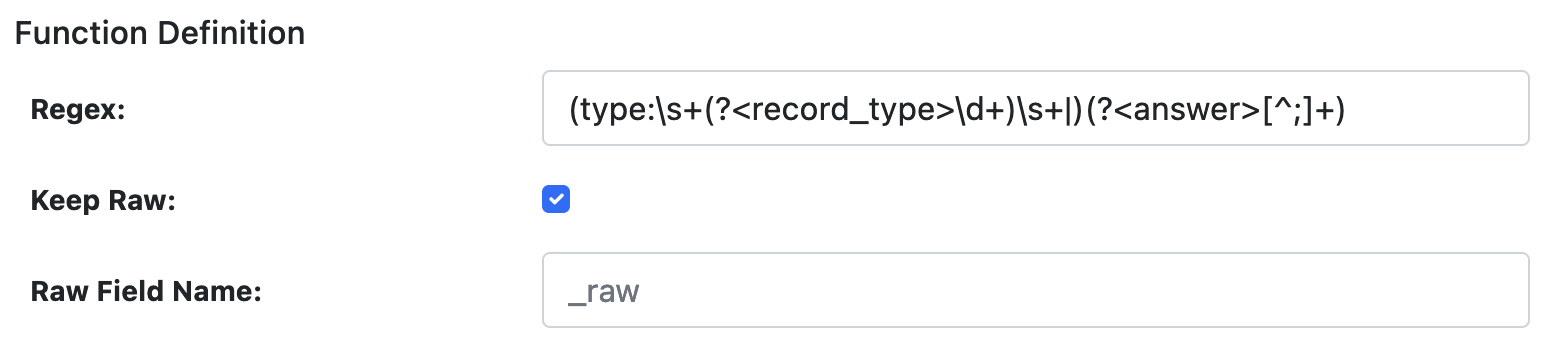
FILTER Definition
This function allows filtering (keep or drop) an event if it matches the specified regular expression (regex) or PDL query (pdl). The event is not transformed and remains the same.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | String | ✓ | Must be pdl or regex. Defines the type of filtering. |
| Value | String | ✓ | Depending on the Type, this must be a PDL query or a Regular Expression to match the event. |
| Action | String | ✓ | When the query/regex matches, this action is processed on the event. Must be keep or drop. |
Example
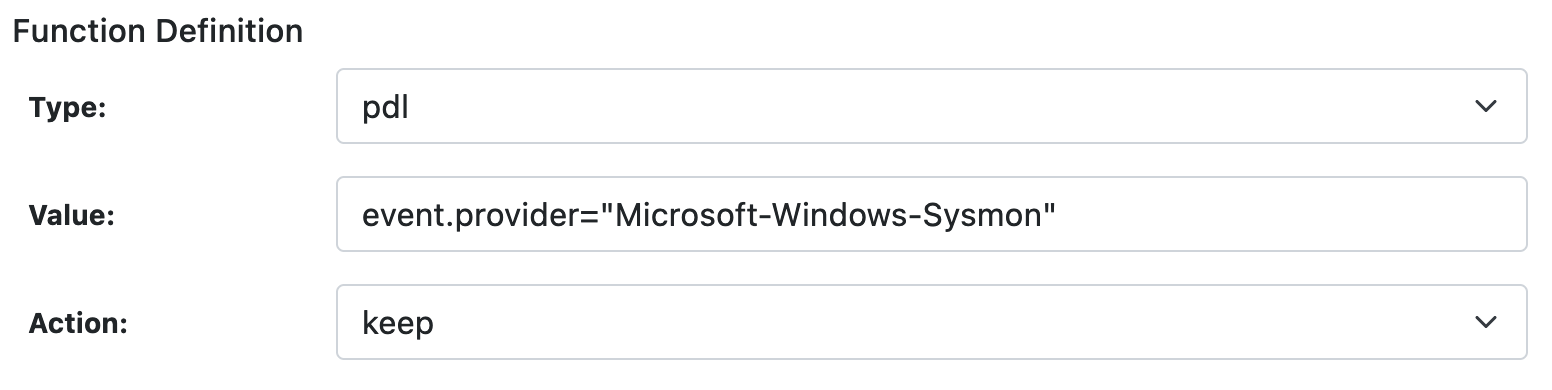
OUTPUT_FIELD Definition
This function outputs the value of a given field. The output is the String representation of the field value.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Field | String | ✓ | Field name from the event data. |
Example

PARSE_CEF Definition
This function allows parsing CEF (Common Event Format) formatted data. The output is a JSON formatted event with specified field names.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keep Raw | Boolean | ✓ | Boolean to keep raw data in a separate field. If set to true, a field name should be provided. |
| Raw Field Name | String | ✗ | If raw data is to be kept, this will be the field to store it in. _raw is the default. |
Example
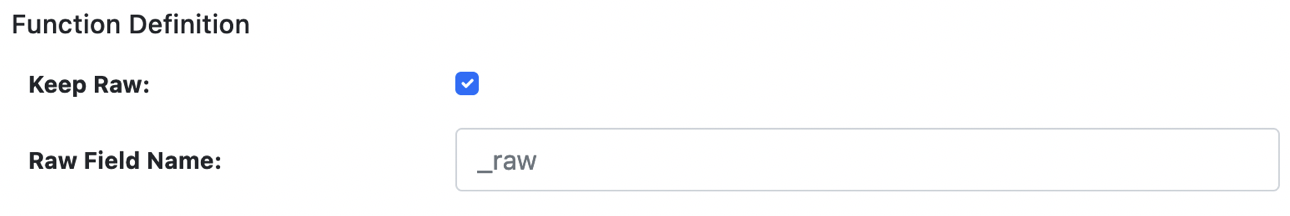
PARSE_CSV Definition
This function allows parsing CSV formatted data with any delimiter. The output is a JSON formatted event with specified field names.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Field Names | String | ✓ | Comma-separated list of field names for the CSV data. |
| Delimiter | String | ✗ | Field separator for the CSV items. Default is comma ,. |
| Keep Raw | Boolean | ✓ | Boolean to keep raw data in a separate field. |
| Raw Field Name | String | ✗ | Field to store raw data if kept. Default is _raw. |
Example
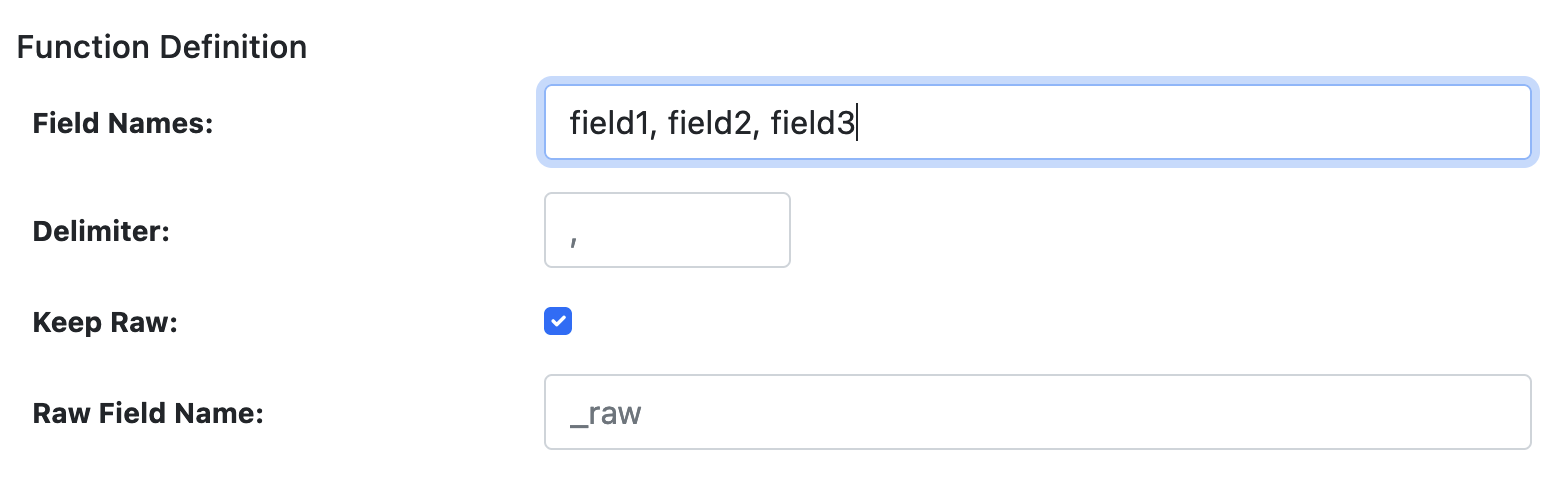
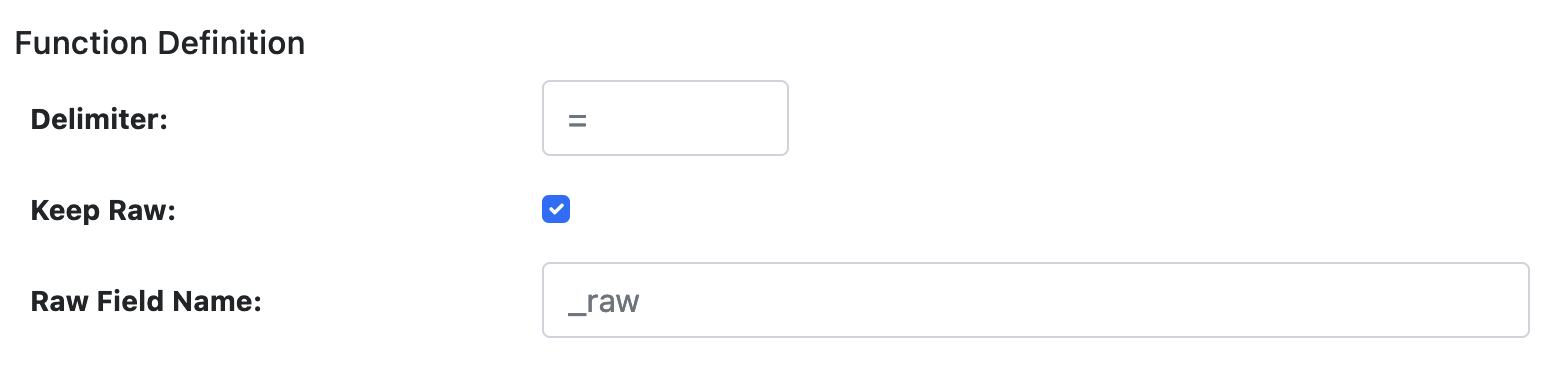
PARSE_KV Definition
This function allows parsing key-value pairs within event data with any delimiter. The left side of the delimiter becomes the field name and the right side becomes the field value. The output is a JSON formatted event.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delimiter | String | ✗ | Field separator for the key-value items. Default is =. |
| Keep Raw | Boolean | ✓ | Boolean to keep raw data in a separate field. |
| Raw Field Name | String | ✗ | Field to store raw data if kept. Default is _raw. |
Example
PDL_EXPRESSION Definition
This function allows data transformation and enrichment via PDL expressions. Input must be in JSON format since fields and conditions require this to process event data.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| pdl | String | ✓ | PDL expression can contain queries, evaluations, field selections, renames, and flatten expressions to transform event data. It also supports lookups for enrichment. See PDL Expression for syntax and usage. |
Example

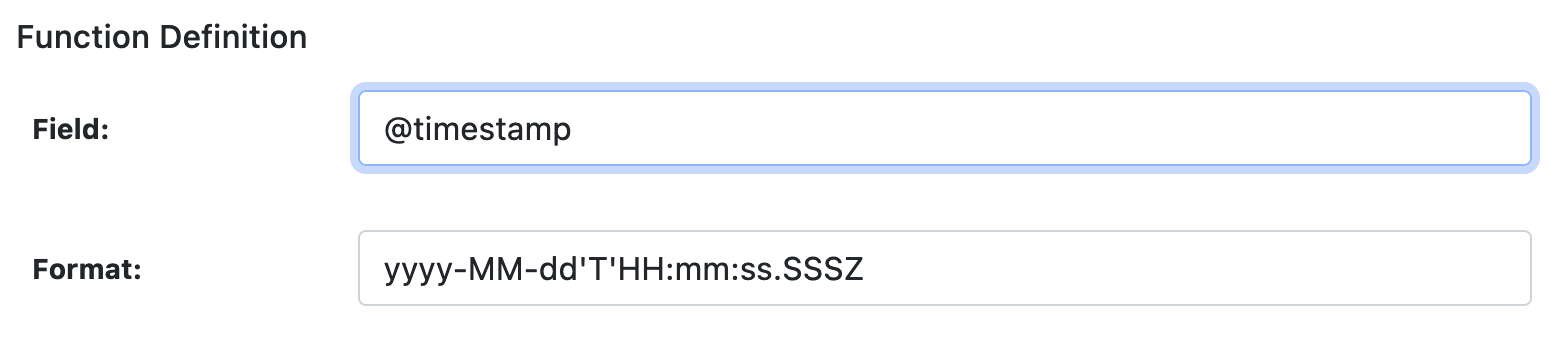
TIMESTAMP Definition
This function extracts an event timestamp from the given field using the provided format. The output is the time in milliseconds in a new field (if specified). The timestamp is used in stream processing.
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Field | String | ✓ | JSON data field name containing the timestamp to parse. |
| Format | String | ✗ | Pattern to extract timestamp based on Java SE DateTimeFormatter. Default: yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZ. |
| Add New Field | Boolean | ✗ | Boolean to add a new field for the extracted timestamp in milliseconds. Default is true. |
| Time Field Name | String | ✗ | Field name for the new timestamp field if Add New Field is true. Default is _time. |
Example
Rules
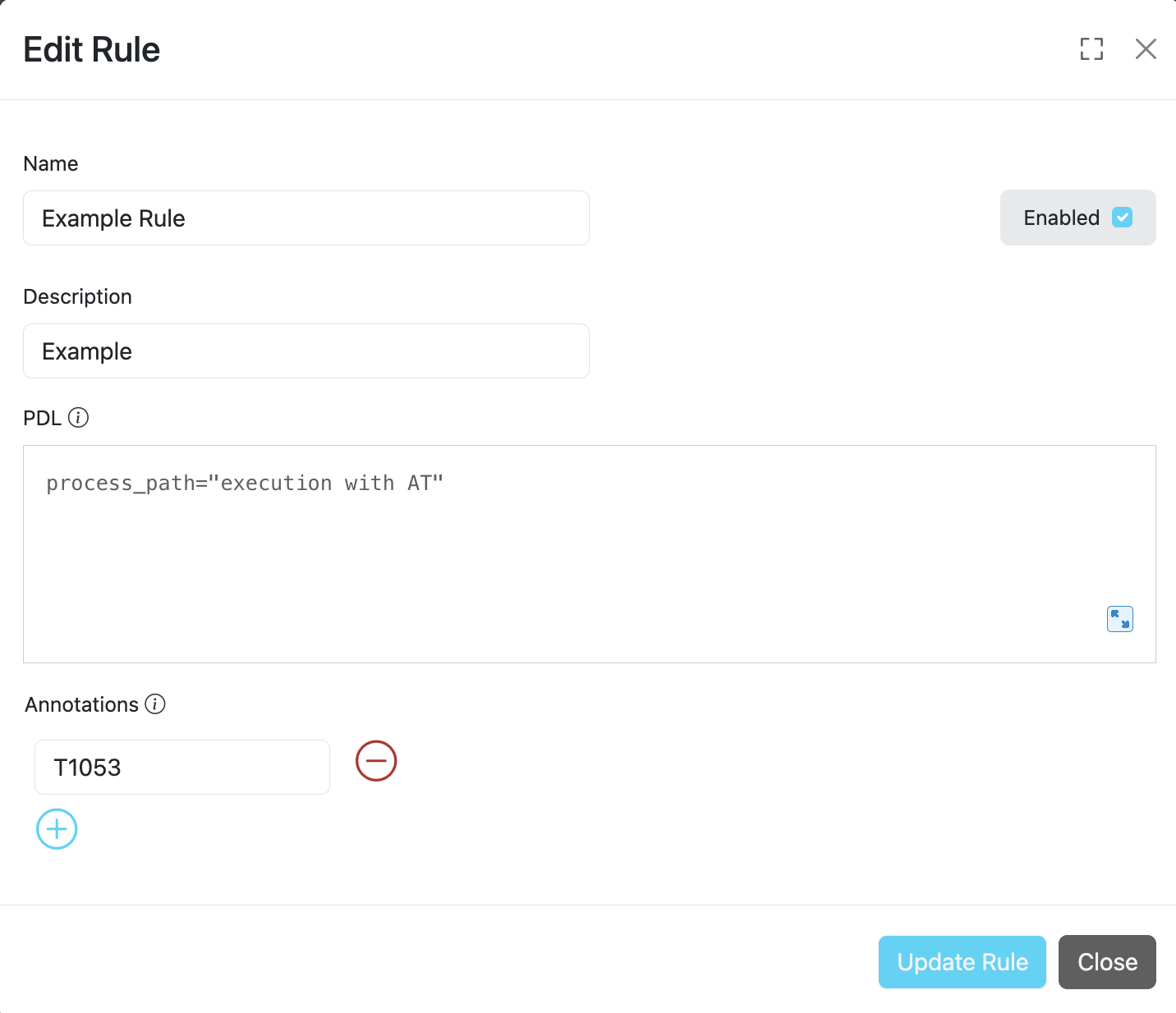
A rule is a PDL Expression or Correlation that performs query matching and/or aggregations on input events. A rule can have additional annotations (e.g. MITRE ATT&CK Technique IDs) for further processing by other analytics systems. We've also created a tool for security practitioners to convert existing Sigma Rules to PDL (see padas-tools repo for details).
The following table describes the configuration fields available for Padas rules:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | String | ✓ | Unique identifier for the rule. This ID is used as a key when updating or deleting the rule entry. |
| Name | String | ✓ | A descriptive name for the rule that helps identify its purpose. |
| Description | String | ✗ | Detailed description explaining the rule's functionality and purpose. |
| PDL | String | ✓ | PDL (Padas Data Language) query to match streaming data. 📖 Reference: PDL Quick Reference 📄 Samples: PadasRules_sample.json |
| Annotations | Array | ✗ | List of applicable annotations for this rule. 💡 Example: MITRE ATT&CK Technique IDs (e.g., T1055, T1071) |
| Enabled | Boolean | ✓ | Controls whether the rule is active. • true = Rule is enabled and will process data • false = Rule is disabled and will be skipped |
Lookups
Lookups enrich your event data by incorporating field-value combinations from lookup tables. Padas uses lookups to compare field-value combinations in your event data with those in external lookup tables. If Padas finds matching field-value combinations in the lookup table, it appends the corresponding field-value combinations from the table to the events in your PDL search results. This process enhances the data and provides you with additional context and insights for analysis.
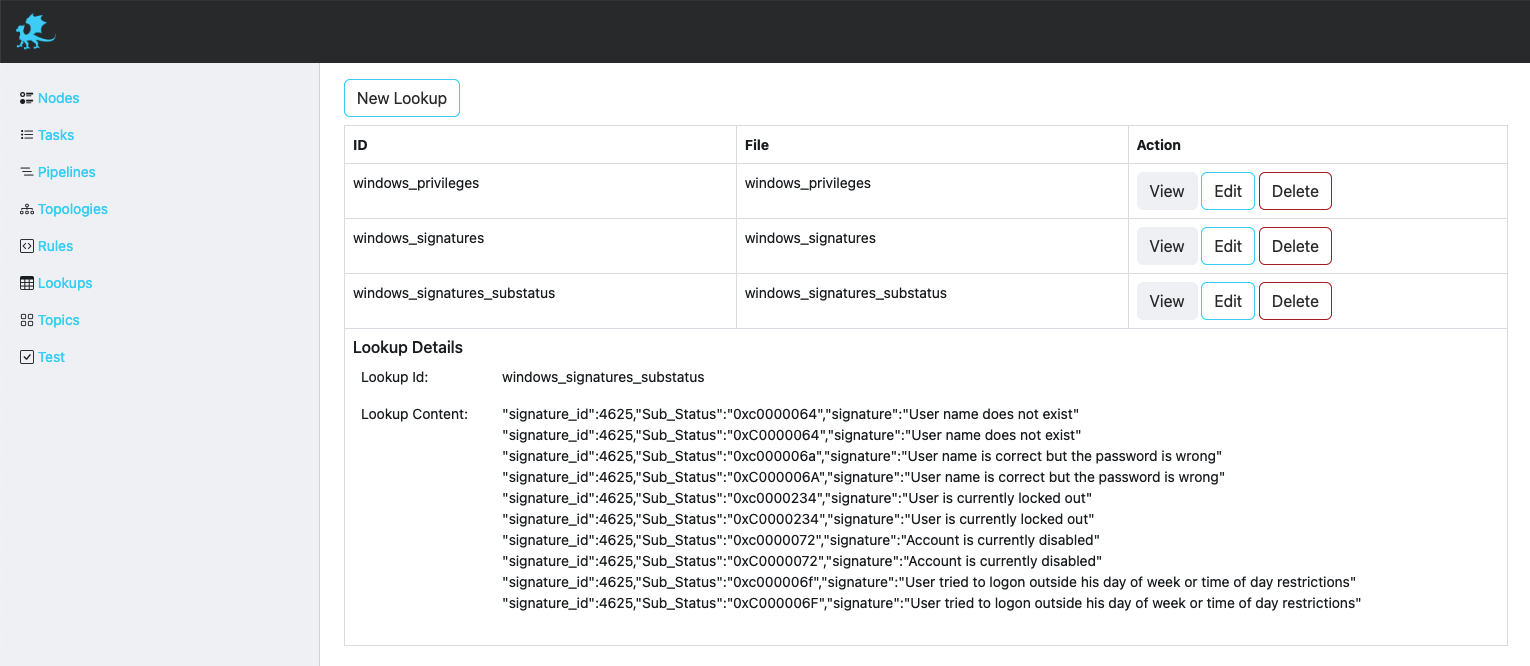
The following table describes the configuration fields available for Padas lookups:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | String | ✓ | Unique identifier for the lookup. This ID is used as a key when updating or deleting the lookup entry. |
| File | File | ✓ | The uploaded lookup file (CSV, JSON, etc.) that contains the reference data for enrichment. Supported formats include CSV, JSON, and other structured data files. |
Test View and Examples
Test view allows a simple interface to play with sample data and verify configurations.
The following table describes the configuration fields available for testing Padas components:
| Field | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test Function | String | ✓ | The functionality to test. Can be a Task, Pipeline, Rule, or PDL. |
| Tasks/Pipelines/Rules | String | ✓ | Based on the Test Function selection, this dropdown lists available/configured options to choose from. |
| Event Data | String | ✓ | Sample event data to test with. Copy/paste your test data here in the appropriate format. |
| Result | Object | - | Output will be displayed under this section showing the test results and any transformations applied. |
Test Process
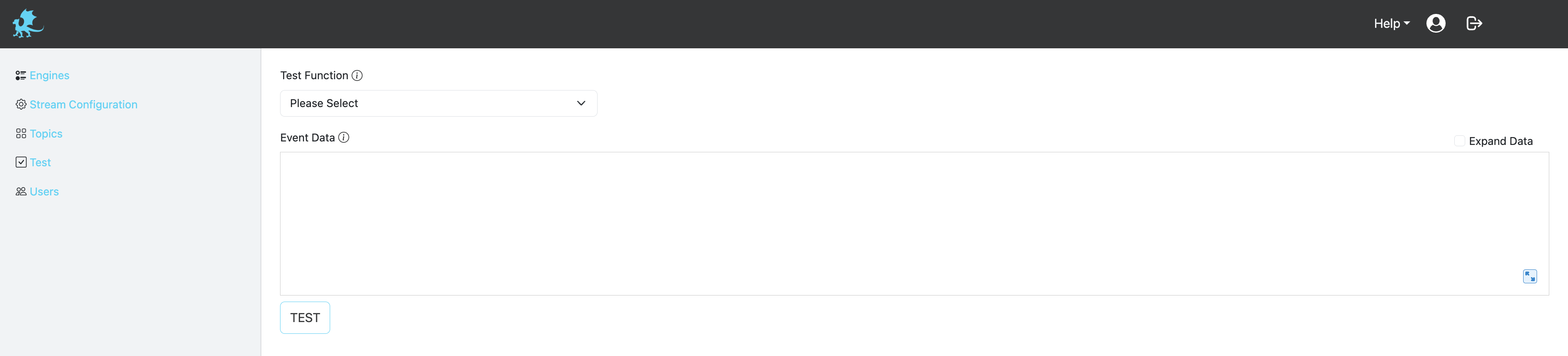
For Task, Pipeline, and Rule Testing:
- Select Test Function: Choose the type of component you want to test (Task, Pipeline, or Rule)
- Select Component: From the dropdown, choose the specific Task, Pipeline, or Rule you want to test
- Enter Event Data: Paste your sample event data in the Event Data field
- Click Test Button: Click the test button to execute the test
- View Results: The test results will be displayed in the Result section showing the output and any transformations
For PDL Testing:
- Select Test Function: Choose "PDL" as the test function
- Enter PDL Expression: Write your PDL expression in the provided field
- Enter Event Data: Paste your sample event data in the Event Data field
- Click Test Button: Click the test button to execute the PDL expression
- View Results: The result of the PDL expression evaluation will be displayed